Internet is Changing and Fast – Hello Web 3.0!
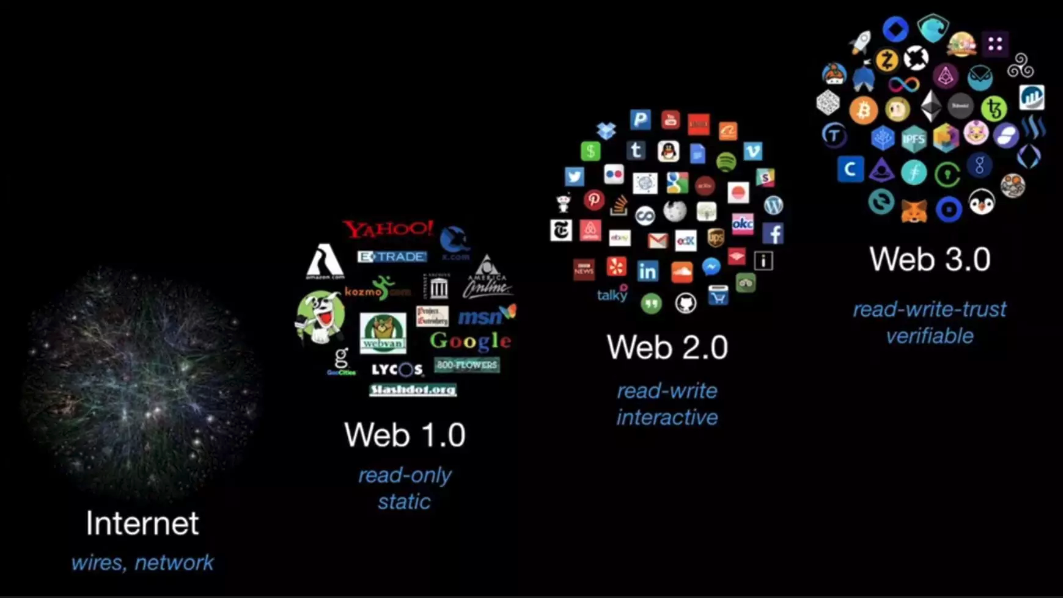
All this while I wasn’t really aware we were on v2.0 of the Internet or the WWW (World Wide Web) until v3.0 came around. And while I really thought its just some protocol and/or a few standards that will have been put into place to pave the way for the new tech i.e faster transmission, better security; Web 3.0 is more than that. It’s all to do with Decentralisation of the Internet.
Up until now it’s always been a Facebook (Meta), Google (Alphabet) or Microsoft behind most of the social, work or communication apps that we use on a daily basis. However by now most of us would be aware of how these applications and companies (mis)use our data and have been selling them to third party organisations or use their ad features and content recommendation algorithms to show us and push us in a specific direction based on the sponsors requirements.
This topic is in itself a blog of its own and I will write one soon however to summarise this has also been a long standing reason to refactor, distribute and decentralise the internet.
Evolution of the Web
The foundation for the internet goes back all the way to 1939 when AT&T used their telephone network to demonstrate the infamous ‘Picturephone’ by sending data over phone lines. This was again shown in 1964. Around the same time ARPA (Advanced Research Projects Agency) of the US Department of Defence laid the ground work that eventually was called ARPANET and much later ‘Internet’ (see source).
Around 1992 the internet had about 1 million hosts, computers and networks had increased their speed and reduced overall cost significantly. The internet evolution started an exponential rise with the birth of the HTTP protocol standards and the emergence of servers and clients paving the way for homepages and any internet presence. When more organisations and engineers got together to drive the internet and what it needs to be, ecommerce and P2P networks were born. I still remember the days of Napster (music sharing app that worked by sharing music using P2P networks) and Orkut (early days social media) that were evolving the internet from just websites to interconnected applications helping to share data. mIRC was an early day Internet Relay Chat tool that was also helping connect people from across the globe.
By 2000 and Y2K ‘kinda impacting the world, engineers persevered through to produce the next generation of social media apps like Facebook and asset sharing apps such as Airbnb and Uber. The next 10 years were spent to improve every layer of technology from hardware capabilities, network speeds and infrastructure, faster and easy software and programming languages, efficient and effective browsers, and the birth of HTTP/2.
However one thing stayed constant and that was the organisations driving this evolution. With every change came a question on how to monetize that change. Our laws and lawmakers attempted to point out the impact of out-dated laws that allow these organisations to flout the very foundations of data and user privacy in each country. But with every deep pocket industry came their lobbyists that were early to ensure the governments acted in their interests and for next 10 years breaches continued until revelations were made by the likes of Edward Snowden and Julian Assange that helped to show the world what the big organisations are doing with our data and how privacy is being breached.
This is where the need for a distributed internet become more important than ever.
Why Web3?
As I have covered the fundamental journey that has led us to the eventual reason why we need to further decentralise the internet above, there were deeper reasons such as ensuring we change the way we see asset ownership. Let us take any digital assets such as artwork, images, videos, any content that is created and used online is fundamentally owned by the organisations. When you sign up with these organisations, the first thing you do is sign their terms and conditions that take away your rights to any of the content that you create. Eventually any photographs you click and attach to the email service that you get for free to send to your friends is now a property of the organisation and hence can be used by them in a way they see fit.
Most people at this point ask – “Yeah my pictures aren’t that important so I’m okay for it to be available on the internet” until this organisation has a tie-up with a third-party and sells this information lets say for research purposes. This research could be into AI that helps to detect and self learn human behaviour and based on this the profile they make of you would be solely based on the images you have taken. Honestly I take an issue with this and hence have been an advocate of owning my data. It is difficult to get to that point due to social pressures of having to be available on social platforms yet I believe that we need to be aware of how things are changing on the internet and choose leaders who understand our interests and push to change and bring law reforms to ensure these organisations are heavily regulated. Another way is ofcourse – Web3
Other reasons of adopting Web3 is to develop an economy based on trustless mechanisms where you do not need to trust a centralised authority or the government (see Blockchain – Evolution of Trust in Cryptoeconomies). Rules are in place and every one needs to follow them and if and when they are followed actions will be executed and results will take place. Imaging being able to create music and share with your fans. A fan is able to use a smart contact to buy or rent your music by simply paying an agreed value that the artist has decided. Once that value is paid, a smart contract would provide access to the music, pay any support platforms such as hosting services and pay the artist.
Moreover if you purchase something of value now that is owned by you. No platform can simply restrict your access and block you on the platform when they feel like it. This helps to resist censorship in the digital world across different platforms and ensures none of them are biased.
In simple words, we need the middle-man gone. But it’s not that easy to achieve this.
Cost and Security
These two terms are the most important terms when it comes to today’s intermediaries. Let’s take an example of any payment system today that has several intermediaries to support the payment network. Each of these intermediaries have high costs that are passed to the consumer. In return they provide you a platform that is secure and can be trusted. But imagine if we were able to reduce the need to have this explicit nature of security and the need for trusted intermediaries replaced with trustless barter.
With Web3 enabling the use of cryptocurrenies, consumers will no longer have to depend on platforms that will use such trusted intermediaries but use systems that will integrate with cyrptocurrencies that will only trade when base rules of engagement are met OR simply said – “I give you X, you give me Y.”
By helping replace these intermediaries we will see significant reduction in operating cost of infrastructure and other associated costs.
I will be adding more content to this blog as I feel to cover more than a ‘What’ and ‘Why’ is important.
Articles on Social Media misuse:
Other great reads:
- How private data of 50 million Facebook users was used to sway elections
- Revealed: 50 million Facebook profiles harvested for Cambridge Analytica in major data breach
- Facebook Acted Too Late to Tackle Misinformation on 2020 Election
- Instagram The Worst As Social Media Slammed As ‘A Gateway For Child Abuse’